| Photo | Name & Title | Contact |
|---|---|---|

|
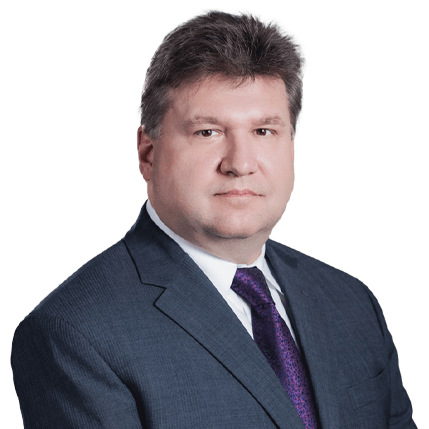
Ronald R. Demsher Principal |
t. 978.202.3405 Email Ronald https://www.hbsr.com/professionals/ronald-r-demsher |

|
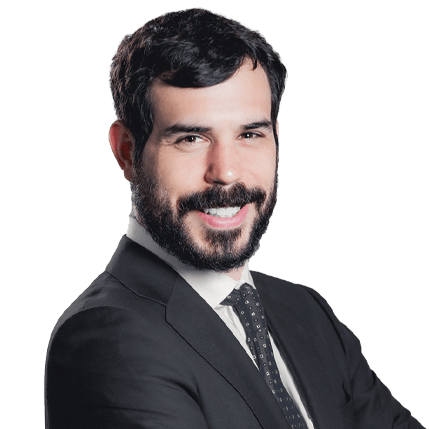
Samuel J. Sussman Principal |
t. 978.202.3421 Email Samuel https://www.hbsr.com/professionals/samuel-sussman |
Quantum technologies are maturing rapidly as they transition from research to real-world deployment across domains such as computing, sensing, cryptography, communications, and materials.
With this comes both unprecedented opportunities for innovation as well as complex intellectual property issues. At Hamilton Brook Smith Reynolds, we have the expertise needed to manage these complex issues.
Why Hamilton Brook Smith Reynolds?
The current patent landscape for quantum computing is highly dynamic and the legal framework for quantum-based innovations is evolving now. This underscores the need for experienced counsel who can articulate how your quantum computing invention provides "technological improvement" and "practical application" beyond an abstract idea.
Our professionals are committed to continuously learning about the evolving technologies and legal structures at the leading edge of quantum research. We understand the nuances of patentability in a field where academic publications often precede patent filings. We work collaboratively with you, ensuring your patent applications are not only scientifically accurate but also legally robust and strategically positioned for long-term value.
In particular, Ronald Demsher and Samuel Sussman, Principals at Hamilton Brook Smith Reynolds, have specific experience in quantum computing. Ron has quantum computing expertise through MIT xPRO, where he completed the two-part Quantum Computing Fundamentals Professional Certificate Program, including coursework in quantum algorithms for cybersecurity, chemistry, and optimization. Sam has assisted clients in protecting cutting-edge inventions, including quantum computing gates and quantum gyroscopes. His background in physics gives him a strong understanding of the mathematical and theoretical foundations of quantum dynamics and its applications.
Our Expertise: Deep Science Meets Cutting-Edge Law
The quantum technology intellectual property landscape demands a unique blend of technical understanding and legal precision. Our team at Hamilton Brook Smith Reynolds is distinguished by:
- Advanced Technical Degrees: Our IP professionals hold advanced degrees in fields critical to quantum computing, including Physics, Electrical Engineering, and Computer Science. This deep technical expertise allows us to grasp the most intricate details of your quantum inventions, from the fundamental quantum mechanics to their practical applications.
- Extensive Industry Experience: Our attorneys, patent agents, and technology specialists have hands-on R&D, design, and software development experience. This practical insight enables us to effectively translate your innovative concepts into robust, enforceable patent claims.
- Proven Track Record: We have a history of successfully navigating complex patent landscapes, including, for example, those related to optics, photonics, and computer hardware – all foundational to quantum computing. We are adept at overcoming challenges such as subject matter eligibility and navigating the rapidly evolving prior art in emerging technologies.
- Strategic IP Counsel: We don't just file patent applications; we develop comprehensive intellectual property strategies tailored to your specific business goals. We understand the interrelationship between quantum technology and intellectual property law and will guide you through the procedures required to protect your innovations.
Areas of Quantum Computing We Can Patent
Our firm is prepared to assist clients in patenting a broad spectrum of quantum computing innovations, such as:
- Quantum Hardware (e.g., various qubit modalities, quantum processors and chips, cryogenic and control systems, quantum gates and circuits, quantum sensors and measurement devices)
- Quantum Software & Algorithms (e.g., quantum algorithms, error mitigation and error correction, hybrid quantum-classical algorithms, quantum operating systems and compilers)
- Quantum Communication & Cryptography (e.g., quantum key distribution systems, post-quantum cryptography implementations, quantum networks)
- Quantum Metrology & Sensing (e.g., quantum sensors, quantum imaging)
- Enabling Technologies (e.g., materials science for quantum devices, advanced cooling technologies, fabrication techniques)